PRACTICAL: Overview of the ARCHER2 system and modules
Overview
Teaching: 20 min
Exercises: 20 minQuestions
What hardware and software is available on ARCHER2?
How does the hardware fit together?
What software is available on ARCHER2 and how can I use it?
Objectives
Gain an overview of the technology available on the ARCHER2 service.
Know how to access different software on ARCHER2 using the module system.
Architecture
The ARCHER2 Cray Shasta system consists of a number of different node types. The ones visible to users are:
- Login nodes
- Compute nodes
- Data analysis (pre-/post- processing) nodes
All of the node types have the same processors: AMD EPYC Zen2 7742, 2.25GHz, 64-cores. All nodes are dual socket nodes so there are 128 cores per node.
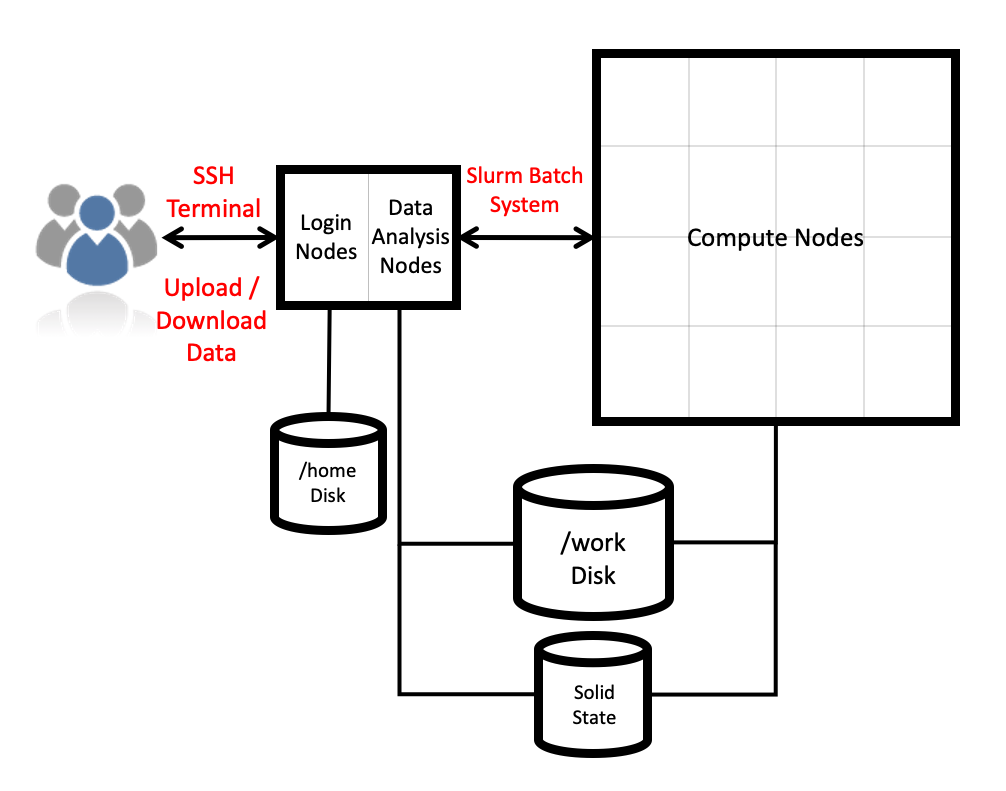
Compute nodes
There are 5,848 compute nodes in total giving 748,544 compute cores on ARCHER2. There are 5,556 standard compute nodes with 256 GiB memory per node and 292 high memory compute nodes with 512 GiB of memory per node. All of the compute nodes are linked together using the high-performance Cray Slingshot interconnect.
Access to the compute nodes is controlled by the Slurm scheduling system which supports both batch jobs and interactive jobs.
Compute node summary:
| ARCHER2 | |
|---|---|
| Processors | 2x AMD EPYC Zen2 (Rome) 7742, 2.25 GHz, 64-core |
| Cores per node | 128 |
| NUMA | 8 NUMA regions per node, 16 cores per NUMA region |
| Memory Capacity | 256/512 GB DDR 3200, 8 memory channels |
| Memory Bandwidth | >380 GB/s per node |
| Interconnect Bandwidth | 25 GB/s per node bi-directional |
Storage
There are three different storage systems available on ARCHER2:
- Home
- Work
- Solid State
Home
The home file systems are available on the login nodes only and are designed for the storage of critical source code and data for ARCHER2 users. They are backed-up regularly offsite for disaster recovery purposes - restoration of accidentally deleted files is not supported. There is a total of 1 PB usable space available on the home file systems.
All users have their own directory on the home file systems at:
/home/<projectID>/<subprojectID>/<userID>
For example, if your username is auser and you are in the project t01 then your home
directory will be at:
/home/t01/t01/auser
Home file system and Home directory
A potential source of confusion is the distinction between the home file system which is the storage system on ARCHER2 used for critical data and your home directory which is a Linux concept of the directory that you are placed into when you first login, that is stored in the
$HOMEenvironment variable and that can be accessed with thecd ~command.
You can view your home file system quota and use through SAFE. Use the Login account menu to select the account you want to see the information for. The account summary page will contain information on your home file system use and any quotas (user or project) that apply to that account. (SAFE home file system use data is updated daily so the information may not quite match the state of the system if a large change has happened recently. Quotas will be completely up to date as they are controlled by SAFE.)
Subprojects?
Some large projects may choose to split their resources into multiple subprojects. These subprojects will have identifiers prepended with the main project ID. For example, the
rsesubgroup of thet01project would have the IDt01-rse. If the main project has allocated storage quotas to the subproject the directories for this storage will be found at, for example:/home/t01/t01-rse/auserYour Linux home directory will generally not be changed when you are made a member of a subproject so you must change directories manually (or change the ownership of files) to make use of this different storage quota allocation.
Work
The work file systems, which are available on the login, compute and data analysis nodes, are designed for high performance parallel access and are the primary location that jobs running on the compute nodes will read data from and write data to. They are based on the Lustre parallel file system technology. The work file systems are not backed up in any way. There is a total of 14.5 PB usable space available on the work file systems.
All users have their own directory on the work file systems at:
/work/<projectID>/<subprojectID>/<userID>
For example, if your username is auser and you are in the project t01 then your main home
directory will be at:
/work/t01/t01/auser
Jobs can’t see your data?
If your jobs are having trouble accessing your data make sure you have placed it on Work rather than Home. Remember, the home file systems are not visible from the compute nodes.
Sharing data with other users
Both the home and work file systems have special directories that allow you to share data with other users. There are directories that allow you to share data only with other users in the same project and directories that allow you to share data with users in other projects.
To share data with users in the same project you use the /work/t01/t01/shared directory
(remember to replace t01 with your project ID) and make sure the permissions on the
directory are correctly set to allow sharing in the project:
auser@login01-nmn:~> mkdir /work/t01/t01/shared/interesting-data
auser@login01-nmn:~> cp -r modelling-output /work/t01/t01/shared/interesting-data/
auser@login01-nmn:~> chmod -R g+rX,o-rwx /work/t01/t01/shared/interesting-data
auser@login01-nmn:~> ls -l /work/t01/t01/shared
total 150372
...snip...
drwxr-s--- 2 auser z01 4096 Jul 20 12:09 interesting-data
..snip...
To share data with users in other projects, you use the /work/t01/shared directory
(remember to replace t01 with your project ID) and make sure the permissions on the
directory are correctly set to allow sharing with all other users:
auser@login01-nmn:~> mkdir /work/t01/shared/more-interesting-data
auser@login01-nmn:~> cp -r more-modelling-output /work/t01/shared/more-interesting-data/
auser@login01-nmn:~> chmod -R go+rX /work/t01/shared/more-interesting-data
auser@login01-nmn:~> ls -l /work/t01/shared
total 150372
...snip...
drwxr-sr-x 2 auser z01 4096 Jul 20 12:09 more-interesting-data
..snip...
Remember, equivalent sharing directories exist on the home file system that you can use in exactly the same way.
Using software modules on ARCHER2
ARCHER2 software modules use the environment modules system to provide access to different software and versions on the system. The modules and versions available will change across the lifetime of the service.
Software modules are provided by both HPE Cray and the ARCHER2 CSE team at EPCC.
What modules are loaded when you log into ARCHER2?
All users start with a default set of modules loaded into their environment. These include:
- Cray Compiler Environment (CCE)
- Cray MPICH MPI library
- Cray LibSci scientific and numerical libraries
- Cray lightweight performance analysis toolkit
- System modules to enable use of the ARCHER2 hardware
You can see what modules you currently have loaded with the module list command:
auser@uan01:~> module list
Currently Loaded Modulefiles:
1) cpe-cray 8) perftools-base/20.09.0(default)
2) cce/10.0.3(default) 9) xpmem/2.2.35-7.0.1.0_1.7__gd50fabf.shasta(default)
3) craype/2.7.0(default) 10) cray-mpich/8.0.15(default)
4) craype-x86-rome 11) cray-libsci/20.08.1.2(default)
5) libfabric/1.11.0.0.233(default) 12) /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env
6) craype-network-ofi 13) /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env-profile
7) cray-dsmml/0.1.2(default)
Getting back if you purge or make a mistake
Unlike many other HPC systems you may have used, you should not generally use the
module purgecommand before starting to use the system. Some of the modules loaded by default are required for you to be able to use the system correctly and so many things will not work if you usemodule purge. If you need to change the setup, you will generally use themodule loadormodule swapcommands instead.If you do find yourself with a broken environment you can usually fix things by logging out and logging back in again.
Finding out what software is available
You can query which software is provided by modules with the module avail command:
auser@uan01:~> module avail
-------------------------------------------------- /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-pyvenvs --------------------------------------------------
tensorflow/2.3.1-py38 torch/1.6.0-py38
--------------------------------------------------- /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-utils ---------------------------------------------------
epcc-job-env lzip/1.20-gcc10 nco/4.9.6-gcc-10.1.0 tcl/8.6.10-gcc10 tk/8.6.10-gcc10 xios/2.5-gcc10 xthi/1.0-gcc10
--------------------------------------------------- /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-libs ----------------------------------------------------
gmp/6.1.2-gcc10 gsl/2.5-gcc10 mpich/3.3.2-gcc10 openmpi/4.0.4-gcc10
--------------------------------------------------- /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-apps ----------------------------------------------------
code_saturne/6.0.5-gcc10 elk/6.8.4 lammps/3_Mar_2020 nwchem/7.0.0 openfoam/org/v8.20200901
cp2k/7.1 gromacs/2020.3 namd/2.14-gcc10 openfoam/com/v2006 quantum-espresso/6.6
--------------------------------------------------------- /opt/cray/pe/perftools/20.09.0/modulefiles ---------------------------------------------------------
perftools perftools-lite perftools-lite-events perftools-lite-gpu perftools-lite-hbm perftools-lite-loops perftools-nwpc perftools-preload
----------------------------------------------------------- /opt/cray/pe/craype/2.7.0/modulefiles ------------------------------------------------------------
craype-hugepages1G craype-hugepages4M craype-hugepages32M craype-hugepages256M craype-network-ofi
craype-hugepages2G craype-hugepages8M craype-hugepages64M craype-hugepages512M craype-network-slingshot10
craype-hugepages2M craype-hugepages16M craype-hugepages128M craype-network-none craype-x86-rome
--------------------------------------------------------------- /usr/local/Modules/modulefiles ---------------------------------------------------------------
dot module-git module-info modules null use.own
--------------------------------------------------------------- /opt/cray/pe/cpe-prgenv/7.0.0 ----------------------------------------------------------------
cpe-aocc cpe-cray cpe-gnu
---------------------------------------------------------------------- /opt/modulefiles ----------------------------------------------------------------------
aocc/2.1.0.3(default) cray-R/4.0.2.0(default) gcc/8.1.0 gcc/9.3.0 gcc/10.1.0(default)
...
The output lists the available modules and their versions. It also shows you which modules are
loaded by default (marked with (default)) when there are multiple versions available and you do
not specify the version when you load.
Licensed software
Some of the software installed on ARCHER2 requires the user to have their licence validated before they can use it on the service. More information on gaining access to licensed software through the SAFE is provided below.
If you want more information on a particular module, you can use the module help command. For example,
to get more info on the cray-netcdf module:
auser@uan01:~> module help cray-netcdf
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Module Specific Help for /opt/cray/pe/modulefiles/cray-netcdf/4.7.4.0:
cray-netcdf
===========
Release Date:
-------------
August 2020
Purpose:
--------
* Update to upstream release 4.7.4.
Product and OS Dependencies:
----------------------------
The NetCDF release is supported on the following systems:
* Cray XC systems with CLE 7.0 UP02 or later
The NetCDF 4.7.4.0 release requires the following software products:
Cray HDF5 1.12.0.*
CrayPE 2.1.2 or later
One or more compilers:
CCE 9.0 or later
GCC 8.0 or later
Intel 19.0 or later
PGI 20.1 or later
Allinea 20.0 or later
AOCC 2.1 or later
Notes and Limitations:
---------------------
Unidata now packages Netcdf-4 and legacy netcdf-3 separately. Cray has
decided not to continue supplying the legacy Netcdf-3 package. Due to CCE
changes a version of netcdf built with "-sreal64" is neither needed nor
provided.
NetCDF is supported on the host CPU but not on the accelerator on
Cray XC systems.
Documentation:
--------------
http://www.unidata.ucar.edu/software/netcdf/docs
Modulefile:
-----------
module load cray-netcdf
OR
module load cray-netcdf-hdf5parallel
Product description:
--------------------
NetCDF (network Common Data Form) is a set of interfaces for array-oriented
data access and a freely-distributed collection of data access libraries for
C, Fortran, C++, Java, and other languages. The netCDF libraries support a
machine-independent format for representing scientific data. Together, the
interfaces, libraries, and format support the creation, access, and sharing
of scientific data.
Loading and switching modules
Lets look at our environment before we change anything. As you may recall, to
see just our loaded modules we use the module list command:
auser@uan01:~> module list
Currently Loaded Modulefiles:
1) cpe-cray 7) cray-dsmml/0.1.2(default)
2) cce/10.0.3(default) 8) perftools-base/20.09.0(default)
3) craype/2.7.0(default) 9) xpmem/2.2.35-7.0.1.0_1.3__gd50fabf.shasta(default)
4) craype-x86-rome 10) cray-mpich/8.0.15(default)
5) libfabric/1.11.0.0.233(default) 11) cray-libsci/20.08.1.2(default)
6) craype-network-ofi
You load modules with the module load command. For example, to load the cray-netcdf module:
auser@uan01:~> module load cray-netcdf
Now, lets list our loaded modules again with module list:
auser@uan01:~> module list
Currently Loaded Modulefiles:
1) cpe-cray 8) perftools-base/20.09.0(default)
2) cce/10.0.3(default) 9) xpmem/2.2.35-7.0.1.0_1.7__gd50fabf.shasta(default)
3) craype/2.7.0(default) 10) cray-mpich/8.0.15(default)
4) craype-x86-rome 11) cray-libsci/20.08.1.2(default)
5) libfabric/1.11.0.0.233(default) 12) /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env
6) craype-network-ofi 13) /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env-profile
7) cray-dsmml/0.1.2(default) 14) cray-netcdf/4.7.4.0
You can see that as well as the default cray-netcdf module (cray-netcdf/4.7.4.0 as we did not specify a version
explicitly).
If you want to swap two versions of the same module then you use the module swap command.
For example, to swap to an older version of GCC, we setup the GNU programming environment
and then swap from the default gcc/10.1.0 module to gcc/9.3.0:
auser@uan01:~> module restore PrgEnv-gnu
auser@uan01:~> module swap gcc gcc/9.3.0
auser@uan01:~> module list
Unloading cray-netcdf/4.7.4.0
Unloading /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env-profile
WARNING: Did not unuse /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-apps
WARNING: Did not unuse /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-libs
WARNING: Did not unuse /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-utils
WARNING: Did not unuse /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse-pyvenvs
Warning: Unloading the epcc-setup-env module will stop many
modules being available on the system. If you do this by
accident, you can recover the situation with the command:
module load /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env
Unloading /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env
Unloading cray-libsci/20.08.1.2
Unloading cray-mpich/8.0.15
Unloading xpmem/2.2.35-7.0.1.0_1.7__gd50fabf.shasta
Unloading perftools-base/20.09.0
WARNING: Did not unuse /opt/cray/pe/perftools/20.09.0/modulefiles
Unloading cray-dsmml/0.1.2
Unloading craype-network-ofi
Unloading libfabric/1.11.0.0.233
Unloading craype-x86-rome
Unloading craype/2.7.0
WARNING: Did not unuse /opt/cray/pe/craype/2.7.0/modulefiles
Unloading cce/10.0.3
Unloading cpe-cray
Loading cpe-gnu
Loading gcc/10.1.0
Loading craype/2.7.0
Loading craype-x86-rome
Loading libfabric/1.11.0.0.233
Loading craype-network-ofi
Loading cray-dsmml/0.1.2
Loading perftools-base/20.09.0
Loading xpmem/2.2.35-7.0.1.0_1.7__gd50fabf.shasta
Loading cray-mpich/8.0.15
Loading cray-libsci/20.08.1.2
Loading /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env
ta005dsh@uan01:~> module swap gcc gcc/9.3.0
ta005dsh@uan01:~> module list
Currently Loaded Modulefiles:
1) cpe-gnu 7) perftools-base/20.09.0(default)
2) craype/2.7.0(default) 8) xpmem/2.2.35-7.0.1.0_1.7__gd50fabf.shasta(default)
3) craype-x86-rome 9) cray-mpich/8.0.15(default)
4) libfabric/1.11.0.0.233(default) 10) cray-libsci/20.08.1.2(default)
5) craype-network-ofi 11) /work/y07/shared/archer2-modules/modulefiles-cse/epcc-setup-env
6) cray-dsmml/0.1.2(default) 12) gcc/9.3.0
Licensed software
For licensed software installed on ARCHER2, users are expected to bring their own licences to the service with them. The ARCHER2 service does not provide software licences for use by users. Access to licensed software is available via three different mechnisms:
- Access control groups - for software that does not support a licence server
- Local licence server - for software that requires a licence server running on the ARCHER2 system
- Remote licence server - to allow software to call out to a publicly-accessible licence server
Getting help with software
You can find more information on the software available on ARCHER2 in the ARCHER2 Documentation at:
This includes information on the software provided by Cray and the software provided by the ARCHER2 CSE Service at EPCC.
If the software you require is not currently available or you are having trouble with the installed software then please contact the ARCHER2 Service Desk and they will be able to assist you.
Key Points
ARCHER2 consists of high performance login nodes, compute nodes, storage systems and interconnect.
There is a wide range of software available on ARCHER2.
The system is based on standard Linux with command line access.
Software is available through modules.